“Aligning EHS and Sustainability” refers to the strategic integration of environmental, health, and safety considerations with broader sustainability initiatives. Traditionally, EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) has focused on compliance with regulations and minimizing risks associated with workplace safety, environmental impact, and health hazards. On the other hand, sustainability encompasses a wider range of concerns, including social responsibility, resource conservation, and long-term viability.
To effectively align EHS and sustainability, organizations should establish clear goals, metrics, and governance structures, as well as foster a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement across departments and functions. This integrated approach requires coordination between EHS professionals, sustainability teams, senior management, and external stakeholders to drive meaningful change and achieve positive outcomes for both business and society.
By aligning following EHS practices with sustainability goals, organizations can achieve several benefits:
Holistic Risk Management
Integrating EHS into sustainability efforts allows organizations to identify and address risks comprehensively, considering not only immediate safety and environmental concerns but also long-term impacts on communities and ecosystems.
Comprehensive Assessment: Integrating EHS into sustainability efforts involves assessing risks and opportunities across the entire value chain. This includes not only internal operations but also supply chain activities, product life cycles, and community impacts.
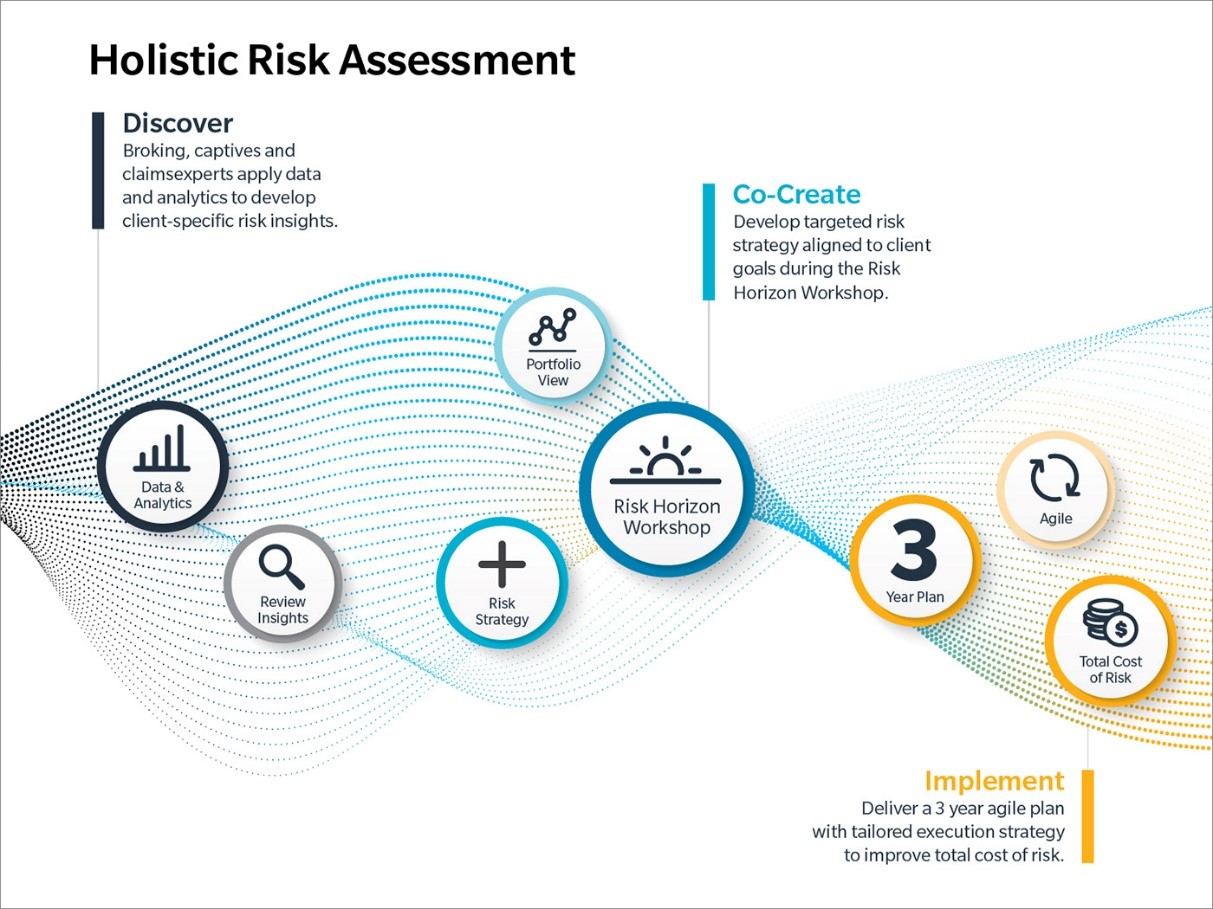
Scenario Planning: By considering a wide range of environmental, social, and economic scenarios, organizations can better anticipate and mitigate potential risks, such as natural disasters, regulatory changes, or reputational crises.
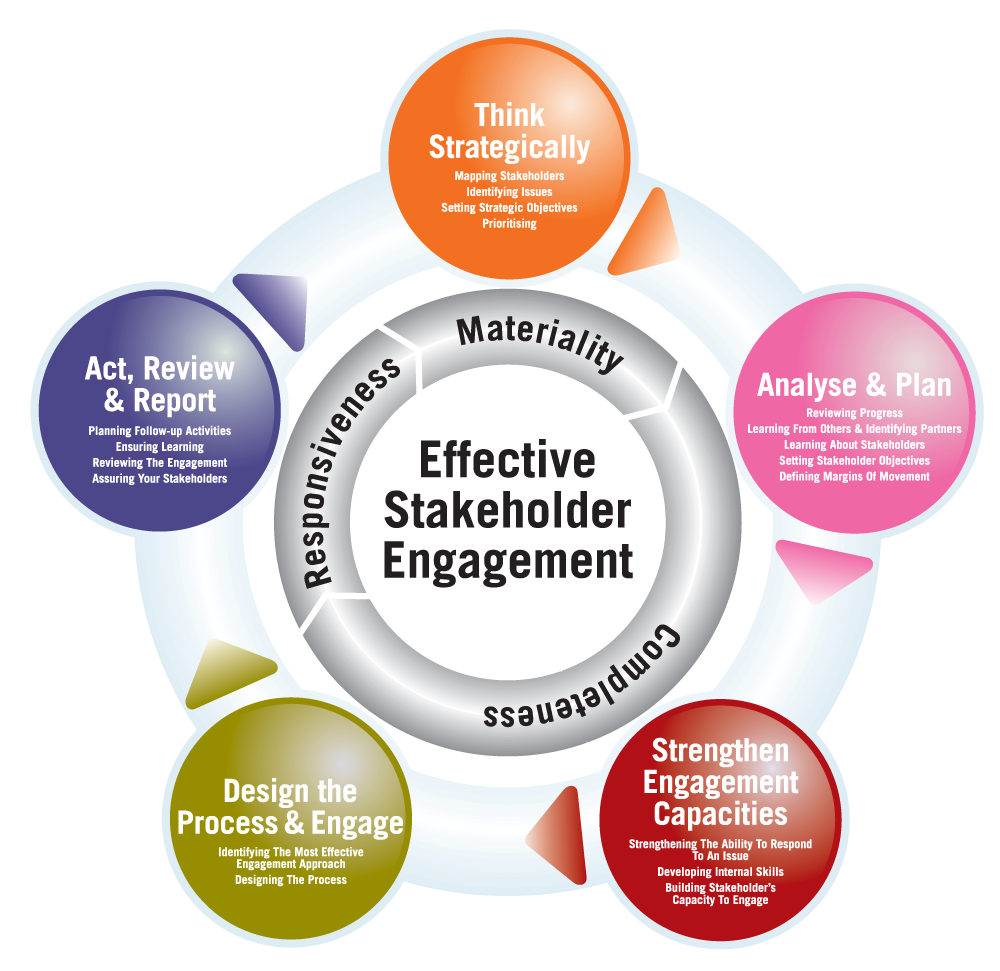
Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with stakeholders, including employees, local communities, NGOs, and regulatory agencies, can help identify emerging risks and priorities, ensuring that EHS and sustainability strategies are aligned with stakeholder expectations.
Operational Efficiency
Sustainability initiatives often lead to improved resource efficiency and waste reduction, which can also have positive impacts on EHS performance. Reducing energy consumption not only lowers carbon emissions but also decreases operational costs and environmental risks.
Resource Optimization: Sustainability initiatives often focus on reducing resource consumption, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy usage. By integrating EHS considerations into these efforts, organizations can achieve cost savings, operational efficiency, and environmental stewardship simultaneously.
Technology Adoption: Leveraging advanced technologies, such as IoT sensors, data analytics, and automation, can enhance EHS performance while supporting sustainability goals. For example, real-time monitoring of air and water quality can help identify and address environmental risks more effectively.
Life Cycle Assessment: Conducting life cycle assessments (LCAs) allows organizations to evaluate the environmental impacts of products and processes from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. This holistic perspective enables informed decision-making and innovation for sustainable product design and manufacturing.
Enhanced Reputation
Demonstrating a commitment to aligning both EHS and sustainability can enhance an organization’s reputation among stakeholders, including customers, investors, employees, and regulators. This can lead to increased trust, brand loyalty, and market competitiveness.
Transparency and Reporting: Communicating EHS and sustainability performance transparently through reports, disclosures, and certifications builds trust with stakeholders and enhances brand reputation. This includes providing accurate and credible information on environmental metrics, safety records, and social initiatives.
Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with stakeholders through dialogue, consultation, and collaboration demonstrates a commitment to responsible business practices and fosters positive relationships. This can lead to increased customer loyalty, investor confidence, and community support.
Risk Management and Crisis Response: Proactively addressing EHS and sustainability issues helps organizations avoid reputational damage and legal liabilities. Effective crisis response mechanisms, such as emergency preparedness plans and stakeholder communication strategies, can mitigate the impact of incidents and build resilience over time.
Regulatory Compliance
Aligning EHS with sustainability strategies helps organizations stay ahead of evolving regulations and compliance requirements. Proactively addressing environmental and social issues can mitigate legal risks and regulatory penalties.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Staying abreast of evolving regulations and standards requires ongoing monitoring and analysis of legislative, regulatory, and industry developments. Organizations should establish mechanisms for tracking compliance requirements and updating policies and procedures accordingly.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Collaborating across functions, such as legal, compliance, EHS, and sustainability, ensure a coordinated approach to regulatory compliance. This includes conducting risk assessments, implementing control measures, and documenting compliance efforts to demonstrate due diligence.

Innovation and Resilience
Aligning EHS with sustainability encourages innovation in product design, manufacturing processes, and supply chain management. By considering environmental and social factors throughout the value chain, organizations can develop more resilient business models that adapt to changing market conditions and stakeholder expectations.
Cross-Sector Collaboration: Collaborating with external partners, such as suppliers, customers, research institutions, and NGOs, fosters innovation and knowledge sharing. By pooling resources and expertise, organizations can develop sustainable solutions to complex challenges, such as climate change, resource scarcity, and social inequality.
Circular Economy Practices: Embracing circular economy principles, such as product reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, promotes resource efficiency and reduces waste. By closing the loop on material flows, organizations can create value from waste streams and minimize environmental impacts throughout the product life cycle.
Sustainable Supply Chains: Assessing and improving the sustainability performance of suppliers helps organizations manage risks, enhance resilience, and drive positive social and environmental outcomes across the supply chain. This includes setting clear expectations, conducting audits, providing capacity-building support, and incentivizing suppliers to adopt sustainable practices.

Long-Term Value Creation
Ultimately, integrating EHS into sustainability efforts enables organizations to create long-term value for shareholders and society as a whole. By balancing economic, environmental, and social priorities, companies can contribute to sustainable development while securing their own success in the global marketplace.
Integrated Reporting: Integrating EHS and sustainability performance into financial reporting provides investors and other stakeholders with a more comprehensive view of organizational value creation. This includes disclosing non-financial metrics, such as carbon emissions, employee safety records, and community engagement initiatives, alongside financial results.
Strategic Alignment: Aligning EHS and sustainability goals with broader business objectives ensures that environmental and social considerations are integrated into strategic decision-making processes. This requires senior management buy-in, cross-functional collaboration, and ongoing performance monitoring to drive continuous improvement and value creation over time.

Stakeholder Value: Ultimately, the alignment of EHS and sustainability contributes to long-term value creation by balancing the interests of shareholders, employees, customers, communities, and other stakeholders. By creating shared value across multiple dimensions—economic, environmental, and social—organizations can achieve sustainable growth and prosperity for all stakeholders.
Summary
Aligning EHS and sustainability involves integrating environmental, health, and safety considerations with broader social, economic, and governance goals to drive responsible business practices and create long-term value for stakeholders and society. This requires a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic issues, as well as proactive engagement with stakeholders and a commitment to continuous improvement and innovation.
Join online courses in OHSE, Fire Safety, Environment and Sustainability, and Mechanical Engineering for professionals to advance their studies alongside their work commitments. Take advantage of the expert faculties and the flexibility of 100% online learning.
Get in touch with us at: info@keneducation.in
Visit our website: www.keneducation.in
Call us on +917569034271
Let’s connect on Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, and Instagram.

