“Health & safety benchmarking” is an important business improvement tool that has been used to imply some form of standard against which can measure performance and quality management in an organization.
A benchmark is a referral point that is generally used in surveying methods.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has defined benchmarking as:
“A planned process by which an organization compares its health and safety processes and performance with others to learn how to reduce accidents and ill health, improve compliance with health and safety law and/or cut compliance costs.”
Benchmarking is an instrument to improve or redesign current health and safety practices by comparing them with other organizations based on the perceptions captured.
Aims Of Benchmarking Process
- Enhance the reputation of organisations with their stakeholders
- Be cost-effective, in terms of avoiding hazards and redesigning the safety practices
- Improve cost-effectiveness in managing risks
- Improve throughout the health and safety system.
- To indicate how you are performing.
- To improve staff engagement and involvement in safety.
- To improve compliance with legislation?
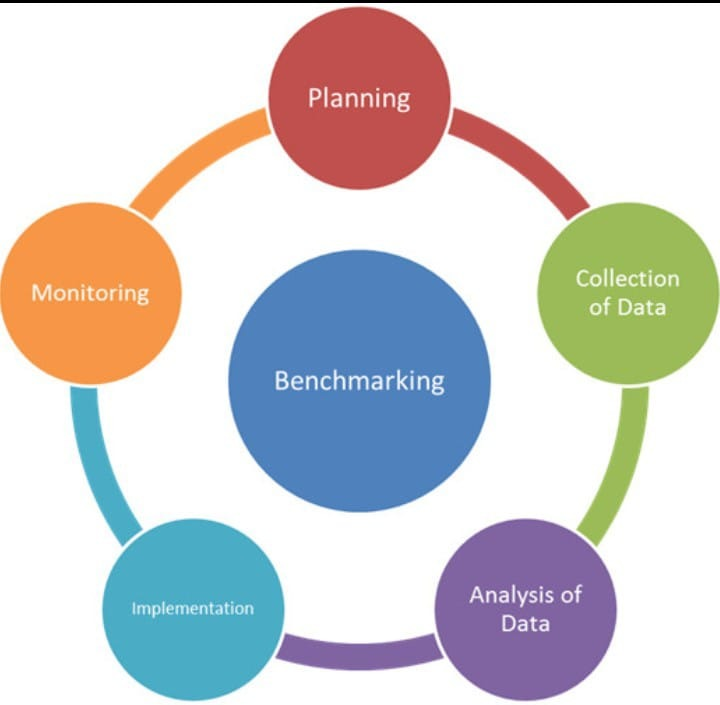
Benchmarking Process
When benchmarking is processed, the first step will lead collection of data that can be benchmarked against industry or government legislation or statistics.
- What is it we want to achieve?
- What or who do we benchmark against?
- What is the cost of benchmarking?
- How will benchmarking improve compliance/performance and reduce costs?
- Measurement of Accident Statistics against recognized standards.
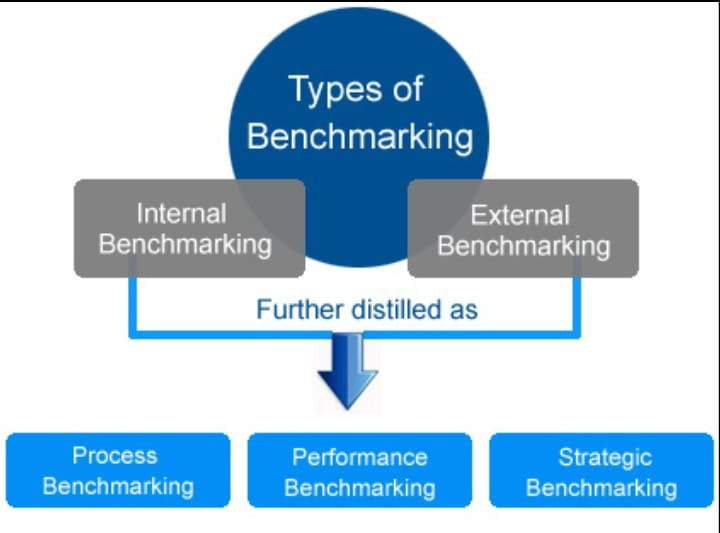
Types Of Health & Safety Benchmarking Process
There are four main types of benchmarking:
- Performance
- Practice.
- Internal
- External
Performance Benchmarking
It is the first step taken to identify performance gaps which involve extracting, collecting, analysing, and comparing quantitative data such as measures or key performance indicators.
This helps in decision-making and identifying performance gaps.

Practice Benchmarking
It is a standard approach for gathering and comparing qualitative information about how an activity is conducted through people, processes, and technology.
This benchmarking process gives insight into where and how performance gaps occur and best practices that can apply in the organization.
Internal Benchmarking
Internal Benchmarking compares performance and practices in various divisions, product lines, units, programs, sectors, etc., within the organization where certain areas of the business are more efficient than others.
It helps to understand the current standard of business performance
External Benchmarking
This process is used to compare the metrics and practices of one organization to other organization/s. here other organizations should agree to participate and to supply the required data.
External Benchmarking helps to understand objectives to be enhanced for the organization and is essential for planning the new strategies.
The biggest benefit comes from external benchmarking as it involves a review of both performance and practice. It creates maximum impact when viewing the world beyond your own desk, department, and organization.
The Five Steps Involved In Health & Safety Benchmarking Process:
Step 1 – Deciding what to benchmark
Benchmarking can be applied to every aspect of health and safety, but it is good practice to prioritize high-hazard and risk areas. Such as the application of hazardous substances and workplace environment or working practices.
To identify these priorities, feedback from the risk assessment and accident data should be used. Consultation with safety personnel and the workforce is also essential.

Step 2 – Deciding the position of your organization
For identifying the current level of performance and improvement in performance, legal requirements have to be considered.
Regulations such as ACOPs and HSE Guidance on the subject and to any statistical information from the organization may also be appropriate to use
Step 3 –partners Selection
to select partners from within the organization, at a different location is internal benchmarking and from outside the organization is external benchmarking.
In the selection of partners, assistance may be taken from local trade associations or the Chamber of Commerce. While selecting partners, ensure compliance with the Benchmarking Code of Conduct.
Step 4 – Working with the partner
The information that is exchanged should be straightforward and comparable. Mutual secrecy should be respected with the right understanding, planning, and preparation as well as with activities and business objectives.
Step 5 –lessons learned and actions taken
Radically, the main objective of the benchmarking process is to learn from other organizations more about the individual organization’s performance.
And comparing with working partners, decide what actions should be taken to improve performance.
According to the HSE, any action plan should be ‘SMARTT’, that is:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Agreed
- Realistic
- Trackable and
- Time bound.
Regular communication and data exchange between partners during the various stages of the Action Plan is the key factor of a successful Health & Safety Benchmarking Process.
At long last, benchmarking is about accepting that there is a scope for your organization to be better at something and to learn how to match!
You’ll never gain that insight if you don’t compare the world beyond your organization.
To brighten your insight around the health and safety topics, join us at info@keneducation.in
visit our website at www.keneducation.in
call +917569034271
Let’s connect on Facebook, YouTube, Linkedin, and Instagram.