Attaining zero workplace accidents is a significant goal for any organization, prioritizing employees’ safety and well-being. Zero Accident Vision is a philosophy that states that nobody should be injured due to an accident. In terms of accident prevention strategies, Vision Zero is more of a philosophy rather than a numerical goal. It is based on the notion that nobody should be injured or killed in an accident. People tend to make errors, but misguided actions should not result in injuries. Zero Workplace Accidents Vision is a way of thinking based on the principle that all accidents are preventable and therefore promoting the Zero Vision is an important strategy for preventing workplace accidents.

Here are the top 10 steps to achieve the goal of attaining zero workplace accidents:
Develop a Comprehensive Safety Plan
Create a detailed safety plan that addresses potential hazards, emergency procedures, and safety protocols. Ensure that it complies with relevant laws and regulations.
Identify all potential hazards in the workplace: This includes physical hazards (e.g., machinery, falls), chemical hazards (e.g., exposure to harmful substances), biological hazards (e.g., exposure to infectious agents), ergonomic hazards (e.g., repetitive strain injuries), and psychosocial hazards (e.g., stress, violence).

Hazard Mapping: Use tools such as site walkthroughs, job safety analysis and safety audits to identify potential hazards. Engage employees in this process, as they are often aware of risks that may not be immediately obvious.
Safety Policies and Procedures: Establish clear safety policies and procedures. Define roles and responsibilities for safety management.
Documentation: Develop clear, written safety policies and procedures. Ensure these documents are easily accessible to all employees.
Communication: Regularly communicate the safety plan to all employees through meetings, newsletters, and posters.
Legal Compliance: Ensure the safety plan complies with local, state, and federal regulations, such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards in the U.S.
Regulations: Stay informed about relevant local, state, and federal safety regulations. Ensure your safety plan incorporates these regulations.
Updates: Regularly update the safety plan to reflect changes in regulations and standards.
2. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Regularly assess the workplace for potential hazards. Identify risks and implement measures to mitigate them. Keep records of assessments and actions taken.
Frequency: Conduct risk assessments regularly, at least annually, or whenever there are changes in operations, equipment, or processes.
Hazard Identification Tools: Use checklists- hazard analysis, hazard and operability studies (HAZOP), failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), root cause analysis (RCA), and job safety analysis to identify potential hazards.
Risk Evaluation: Assess the likelihood and severity of identified risks. Prioritize risks that require immediate attention.
Special Assessments: Perform additional assessments whenever there are changes in operations, new equipment is introduced, or after an incident.
Employee Input: Involve employees in the identification process, as they often have valuable insights into potential hazards.
Risk Evaluation: Scoring: Evaluate risks based on their likelihood and potential severity. Use a risk matrix to prioritize high-risk areas.
Mitigation Plans: Develop and implement mitigation plans for identified risks. Regularly review and update these plans.
3. Provide Safety Training
Offer regular and thorough safety training to all employees. Training should cover general workplace safety as well as job-specific hazards. Update training materials as necessary. The following three types are crucial for employees to attain zero workplace accidents
- Orientation Training: Ensure all new employees receive comprehensive safety training during their orientation.
- Ongoing Training: Provide ongoing training sessions to keep employees updated on safety protocols and new hazards.
- Specialized Training: Offer specialized training for high-risk tasks, such as operating heavy machinery, handling hazardous materials, or working at heights.

- Orientation Training:
New Hires: Ensure all new employees receive comprehensive safety training as part of their onboarding process.
Refresher Courses: Provide refresher training periodically to reinforce safety concepts.
- Ongoing Training:
Regular Sessions: Regular safety training sessions keep employees updated on new hazards, equipment, and procedures.
Interactive Methods: Use interactive training methods such as simulations, hands-on practice, and e-learning modules to engage employees.
- Specialized Training:
High-Risk Tasks: Provide specialized training for tasks that involve high risk, such as operating heavy machinery, handling hazardous materials, or working at heights.
Certification: Ensure employees are certified to perform specific high-risk tasks where required by law or industry standards.
4. Promote a Safety Culture
To Attain a Zero Workplace Accident culture, encourage employees to report unsafe conditions and behaviors without fear of reprisal. Recognize and reward safe practices.
Leadership Commitment: Ensure that leadership demonstrates a commitment to safety. Leaders should visibly support safety initiatives by participating in safety meetings, conducting walk-throughs, and addressing safety concerns.
Resource Allocation: Allocate sufficient resources (time, money, personnel) to safety programs.
Employee Engagement: Encourage employees to take ownership of safety. This can be done through suggestion programs, safety committees, and open-door policies for reporting safety concerns and decision-making processes.
Open Communication: Foster an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting safety concerns without fear of retaliation.
Recognition Programs: Through rewards and feedback: Implement programs to recognize and reward safe behaviors and practices, such as safety awards, bonuses, and public recognition. Provide regular feedback to employees on their safety performance and areas for improvement.
5. Implement Safety Protocols
Establish and enforce clear safety protocols and procedures for all tasks. Ensure that employees understand and follow these protocols.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop detailed SOPs for all tasks, clearly outlining safe methods to perform work. Regularly review and update SOPs to reflect changes in processes, equipment, or regulations.

- Signage and Labels: Use clear and visible signs, labels, and posters to remind employees of safety procedures and potential hazards. Ensure all signage and labels comply with relevant standards and regulations.
- Enforcement:
- Supervision: Ensure supervisors and managers consistently enforce safety protocols.
- Accountability: Hold employees accountable for following safety procedures. Address non-compliance promptly.
6. Ensure Proper Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is the most important Key to attain zero workplace accidents. Provide appropriate PPE for employees and ensure they are trained on its correct usage and maintenance.
PPE Assessment: Identify the necessary PPE for different tasks and ensure it is available to employees. Regularly inspect PPE for wear and tear and replace it as needed.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect PPE to ensure it is in good condition and replace it when necessary.
- Needs Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis to determine the PPE required for different tasks.
- Accessibility: Ensure PPE is readily available to all employees who need it.
- Regular Checks: Conduct regular inspections of PPE to ensure it is in good condition.
- Replacement: Replace damaged or worn PPE promptly to maintain protection.
- Training:
- Usage: Train employees on the correct usage, care, and maintenance of PPE.
- Inspection: Teach employees how to inspect PPE for damage and wear and when to replace it.
7. Maintain Equipment and Machinery
To attain the Zero Workplace Accidents Vision, regularly inspect, maintain, and repair all equipment and machinery to ensure they are in safe working condition. Follow manufacturers’ guidelines for maintenance.
- Preventive Maintenance: Implement a preventive maintenance program. Ensure that all equipment is used according to manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines.
- Schedules: Develop and follow preventive maintenance schedules for all equipment and machinery.
- Records: Keep detailed records of maintenance activities and repairs.
- Safe Operation:
- Training: Ensure all operators are trained on the safe use of equipment and machinery.
- Compliance: Ensure equipment is used according to manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines.
- Repairs:
- Timely Repairs: Promptly address any issues with equipment and machinery promptly to prevent malfunctions that could lead to accidents.

- Qualified Technicians: Use qualified technicians to perform repairs and maintenance.
8. Encourage Employee Involvement
Involve employees in safety planning and decision-making. Create safety committees and encourage employees to participate in safety meetings and initiatives.
- Engagement Activities: Organize safety awareness events, workshops, and competitions to keep safety top of mind. Offer incentives for participation in safety activities, such as recognition awards or small prizes.
- Safety Committees: Form safety committees with representatives from different departments to discuss safety concerns and solutions. Hold regular safety committee meetings to review incidents, suggest improvements, and share best practices.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Provide multiple channels to give feedback on safety issues, such as suggestion boxes, safety hotlines, and anonymous surveys.
- Follow-Up: Act on employee feedback promptly and communicate the actions taken.
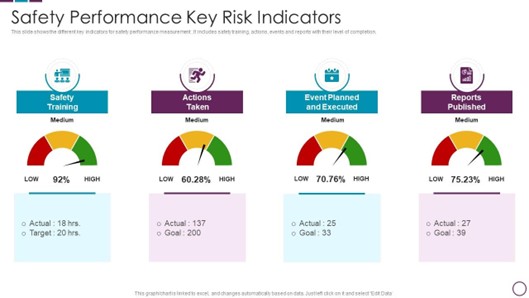
9. Monitor and Review Safety Performance
Safety Performance Metrics helps to attain Zero workplace Accidents. Regularly review and update safety policies based on findings.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review safety data to identify trends and areas for improvement. Update safety policies and procedures based on findings. Use this data to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Metrics: Track key safety performance indicators (KPIs), such as incident rates, near-misses, and the number of safety observations. Compare performance metrics against industry benchmarks and standards.
- Incident Investigation:
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigate all accidents and near-misses to determine root causes and implement corrective actions.
- Reporting: Maintain detailed incident reports and review them regularly to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
10. Prepare for Emergencies
To attain Zero Workplace Accidents Vision that nobody should be injured due to an accident we should develop and regularly update an emergency response plan.
- Emergency Equipment: Ensure that emergency equipment, such as fire extinguishers, first aid kits, and evacuation maps, are readily accessible and well-maintained.
- Training: Train employees on the proper use of emergency equipment and procedures.
- Emergency Plans:
- Scenarios: Develop emergency response plans for various scenarios, such as fires, chemical spills, natural disasters, and medical emergencies.
- Roles: Define roles and responsibilities for emergency response teams.
- Drills:
- Frequency: Conduct regular emergency drills to ensure employees know how to respond and where to go in case of an emergency.
- Evaluation: Evaluate the effectiveness of drills and make necessary improvements to emergency plans.
By implementing these steps, organizations can create a safer workplace and move closer to achieving zero workplace accidents. Vision Zero plays a pivotal role in eliminating work-related injuries and fatalities. This entails reinforcing a culture of prevention within organizations and among individual workers.
Every workplace injury, illness, or death is preventable, and we can make that possible through education and awareness.
Join Ken Institute and unlock a world of online courses in Occupational Health and Safety, Fire Safety, Environment and Sustainability, and Mechanical Engineering. Propel your career to new heights.
Get in touch with us at: info@keneducation.in,
Visit our website www.keneducation.in
Call us on +917569034271
Let’s connect on Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, and Instagram.